Quick Grading Mercury Dimes
Posted by Tom Deaux on Oct 1st 2020
Why Quick Grading?
Determining a reasonably accurate grade quickly can pay off. Here are two examples:
1)There are times when slow, careful deliberation over the grade of a coin is not an option.
Let’s say you’re at coin show and you see a coin that you’d like to buy. The coin is graded by the seller; is it an accurate grade? A quick grade will help you approximate the value of the coin on the spot.
2)You have 100 inexpensive coins to sell. Quick grading will save you time pricing them for sale.
Obviously, quick grading is not recommended for expensive coins as making a mistake in that realm can be costly.
High Points on the Mercury Dime
The highest points on the Mercury Dime, obverse and reverse, are shown here. These are the areas where the coin will show wear first.
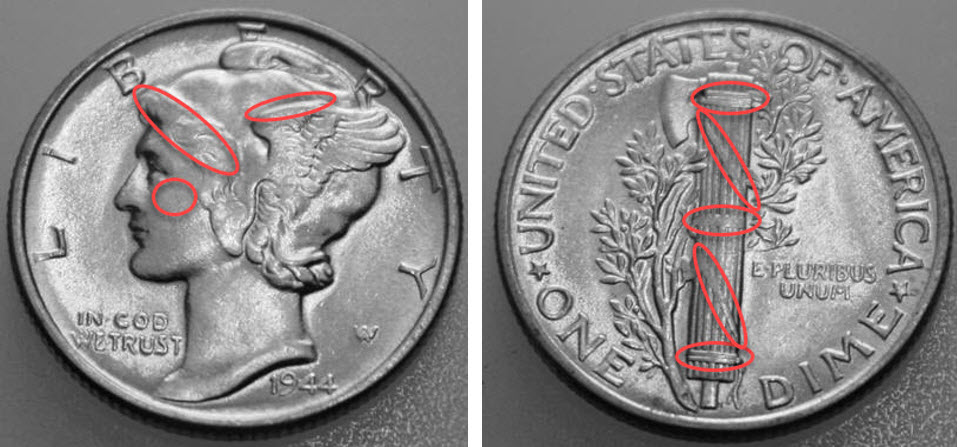

Where to Focus for a Quick Grade
The fasces on the reverse tells a lot about the coin’s overall wear. There are three sets of horizontal bands on the fasces; top, middle, and bottom. There are two diagonal bands.
The Center horizontal band is often weak due to the strike, so use the top and bottom horizontal bands and the diagonal bands to measure wear.

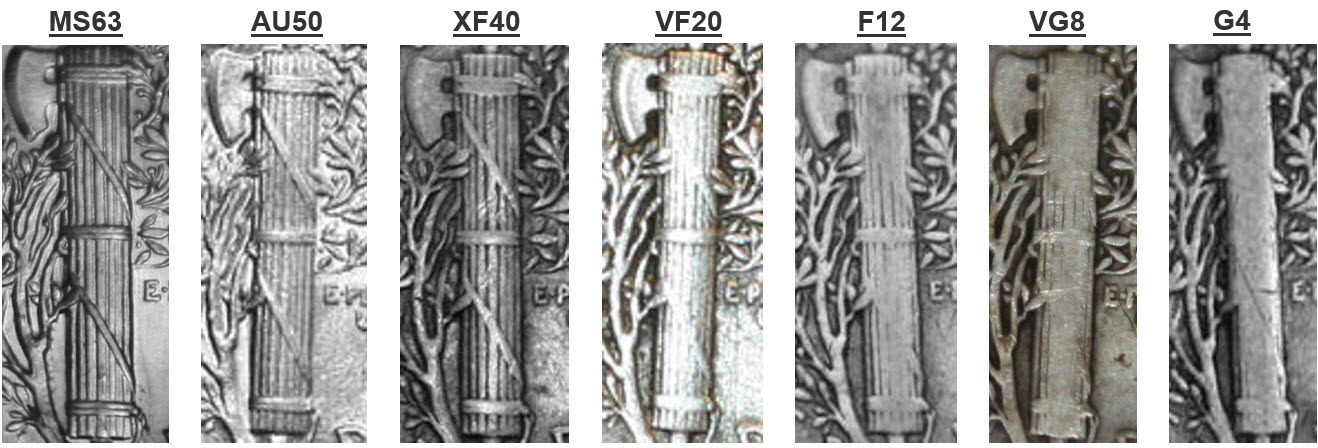
Quick Grade
Here are some examples of what the fasces of a Mercury Dime looks like in various grades, from Uncirculated MS-63 down to Good-4. You can use these images to practice grading coins in hand until you’re familiar with what the fasces looks like in various grades.
Once you’re familiar with what the fasces looks like through the wearing process, it is easy to assign a quick grade for mercury dimes. You can look at the front and back of the coin overall, then assign a grade based on the appearance of the fasces. The grade can be adjusted if there are other positive or negative features on the coin, for example if the coin is struck very well or if there are problems like discoloration, scratching, or rim damage.
Professional Coin Grading Service PCGS has a free service online called PCGS Photograde. This application allows you to see what various US coins (including Mercury Dimes) look like as they are gradually worn from New Uncirculated down to Poor-1. Using this service will help you to hone your skill in grading coins overall.
About Uncirculated vs Uncirculated Coins
Most grades should be fairly easy to determine based on the amount of wear on the fasces.
There is one area where it is a little more involved. When the coin looks brand new, it could be About Uncirculated (Grade 50 to 58) or Uncirculated (Grade 60 and up). The differences in appearance are small, but they can make a big difference in the value.
Look at the high points under a light and rock the coin back and forth. You will see either; Uninterrupted mint luster, or a break in the luster where there is wear. A break in the luster means the coin is not Uncirculated. Grading these coins accurately will take some practice.
Full Split Bands
If the coin is in the About Uncirculated to Uncirculated range, you’ll want to check to see if the coin has Full Split Bands. Full Split Bands designates that the coin was struck well and has a lot of detail, because the center of the reverse is the part of the coin that loses detail first when the die begins to wear.
Look at the center bands on the Fasces under magnification to see if the two bands are separated all the way across. If so, the coin should be designated as having “Full Split Bands”, and the coin will increase in value.
When to Deduct Valuation
After you determine your quick grade, re-examine the coin front and back and look for problems, for example:
> Scratches, gouges, pits, holes, etc.
> Rim damage
> Discoloration
> And so on
If you find problems, you should lower the price accordingly. This is a qualitative evaluation; you’ll improve with experience.
Review
Determining a reasonably accurate grade quickly can have its rewards. Knowledge in this area of the hobby will pay off over time.
- 1) Look at both sides of the coin; then focus on the fasces
- 2) If the coin is in the AU to Uncirculated range, check for Full Split Bands
- 3) Use the higher value in the price guide for Full Split Bands
- 4) Check the coin for defects and decrease the value if appropriate
Happy Grading!
